INSTRUMENTS
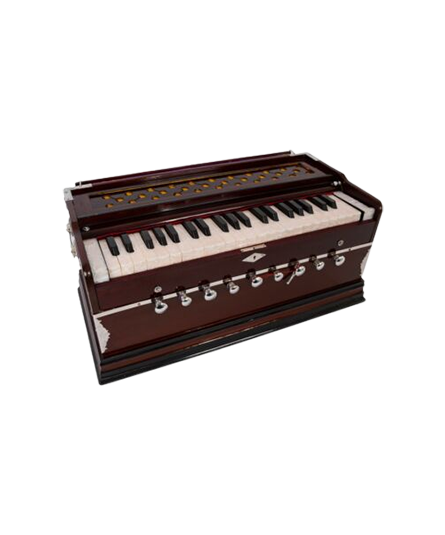

Harmonium
Harmonium is a stringed instrument made of wood, metal, brass, and cloth. A kind of a portable wooden box, it was originated in West Bengal. The harmonium has thus become an integral part of Indian Music. It is extensively used to accompany folk, classical, Sufi, and ghazal compositions for both music and dance.
The keys are played and bellows are compressed simultaneously . When the bellows are compressed, the air passes through the reed, causing it to vibrate. This produces sound. The reed regulates the tone/pitch whereas the bellows produce and control air and the volume. The harmonium can produce up to 12 surs and 22 shrutis.
Dilruba
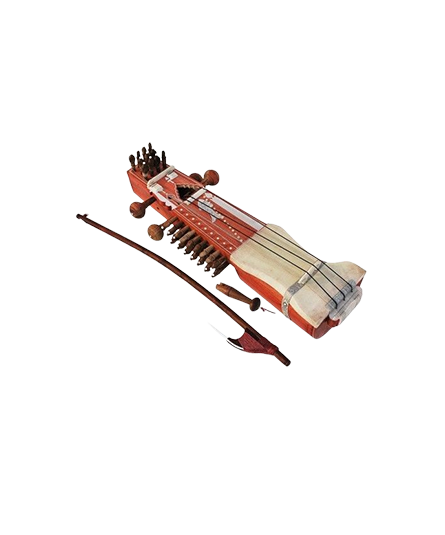
Dilruba is a stringed instrument, made of metal, parchment, and horsehair. Used in religious ceremonies, this instrument is found in different parts of North India. Majorly used as a solo as well as an accompanying instrument in Northern Classical music. Also popularly used as an accompanying instrument to Gurbani.
A fretted bowed instrument with a parched resonator and a flat fingerboard. Four main metal strings, twenty sympathetic strings and nineteen elliptical frets. Played with a horse hair bow. Used as a solo as well as an accompanying instrument in Northern Classical music. Also popularly used as an accompanying instrument to Gurubani.
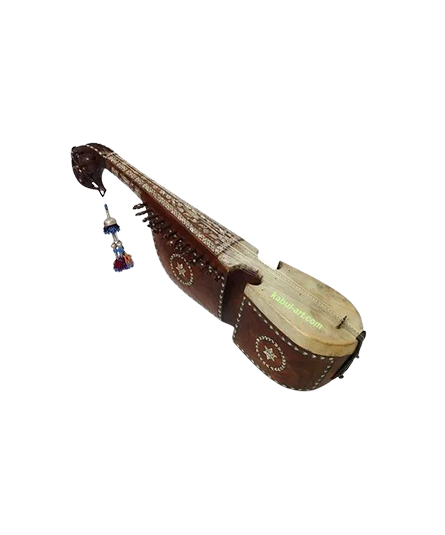


Rabab
Rabab is a stringed instrument made of wood, parchment, and steel. This traditional instrument is found in Jammu and Kashmir. Majorly used in ‘Chakkari’, ‘Sufiyana Qalam’, and other folk forms of Kashmir.
A partially fretted plucked instrument. Made out of a single block of wood. Skin covered resonator, having side depressions; a long narrow fingerboard with an arched peg box. Six main playing strings & gut and eleven sympathetic steel strings plucked with the help of plectrum held in right hand. Used in ‘Chakkari’, ‘Sufiyana Qalam’ and other folk forms of Kashmir.
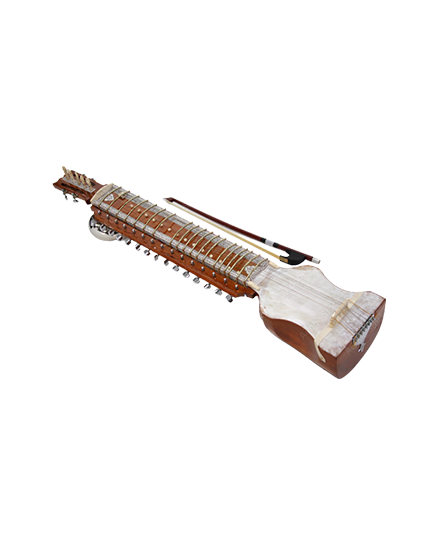
Sarangi
Sarangi is a stringed instrument made of wood, steel, snakeskin, and horsehair. This traditional instrument is found in many parts in North India and is a popular instrument in Bihar. Majorly used as a prominent accompaniment to the vocalists in Northern Indian Classical music, and also for solo performance in North India and is used in folk and traditional music in Bihar.
A bowed instrument scooped out of a single log of wood. Three main playing strings of gut, of varying thickness. Thirty seven sympathetic steel strings. Played with a bow made of horsehair. Strings are stopped not by fingertips but by the base of the nails. Used as a prominent accompaniment to the vocalists in Northern Indian Classical music, and also for solo performance.
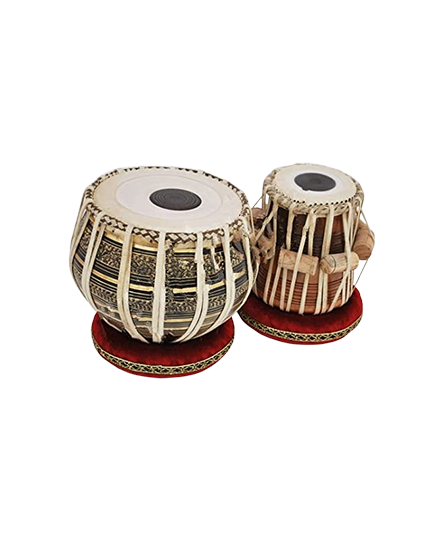

Tabla
Tabla is a percussion instrument made of wood, metal, brass, cloth, clay, copper, aluminum, steel, rice, wheat, charcoal powder, plant fiber, iron, nickel, gum, soot, buffalo skin, goatskin, leather, and glue. This is a traditional instrument that is found in various parts of North India. It is an important rhythmic accompaniment to solo and instrumental music ensembles as well as a solo performance instrument.
Tabla has a complex playing technique. It involves extensive use of fingers and palms which produces a wide variety of different sounds and rhythms called mnemonic syllables (bol). It is played in two ways- band bol (tali) and khula bol (khali).
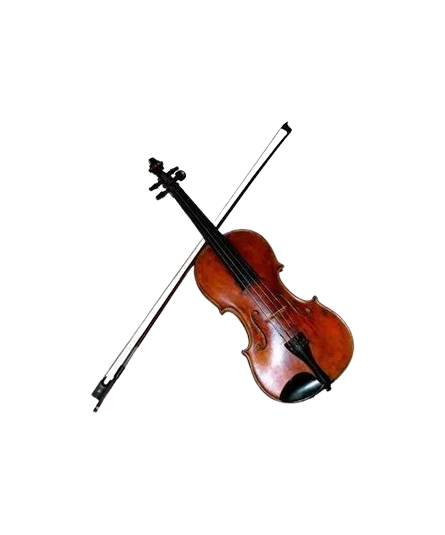
Violin
The Violin instrument is one of the best known and most widely played instruments in the world. The Violin instrument is a bowed instrument in the string family. It has a body made from multiple types of wood and features a fretless fingerboard on the neck. The strings are attached to tuning pegs on one end and to a tailpiece passing over a bridge on the other. The bridge transmits the strings’ vibrations to the hollow body of the instrument, which amplifies the sound.
